Blog
Introduction
Proper maintenance is essential for every building to preserve its integrity, ensure functionality, and provide comfort to its occupants. Maintenance comes in several types and approaches, but the two most common types of maintenance would be preventive and reactive maintenance. Preventive maintenance approach aims to prolong asset lifespan by tackling wear and tear before it develops into a problem [1]. While on the other hand, reactive maintenance involves delaying or ignoring early signs of failure, which can result in premature asset breakdowns and expensive equipment replacements [1]. For this article, we will discuss two type of maintenance in detail, along with their benefits and drawbacks.
Overview of Preventive Repairs
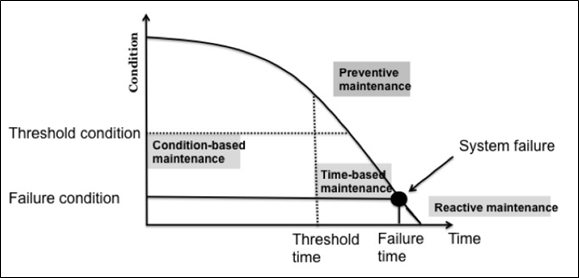
Preventive maintenance refers to the regular or scheduled maintenance performed in order to avoid major break down or damage. Preventive maintenance action are often less expensive than reactive maintenance activities. The primary objective of preventive maintenance is to prevent failures in a cost-effective manner [2]. This type of maintenance is conducted before any failure occurs and within acceptable thresholds, as illustrated in Figure 1, in order to prevent significant damage from happening..
Overview of Reactive Repairs
Reactive maintenance, on the other hand, is performed only after a failure occurs. This type of maintenance is unplanned and is only applied to a component when it is necessary to restore the system to operational status [2]. Reactive maintenance occurs when the system falls below a threshold condition and approaches a failure state, as illustrated in Figure 1. This approach can lead to higher maintenance costs and disrupt daily operations due to unexpected repairs.
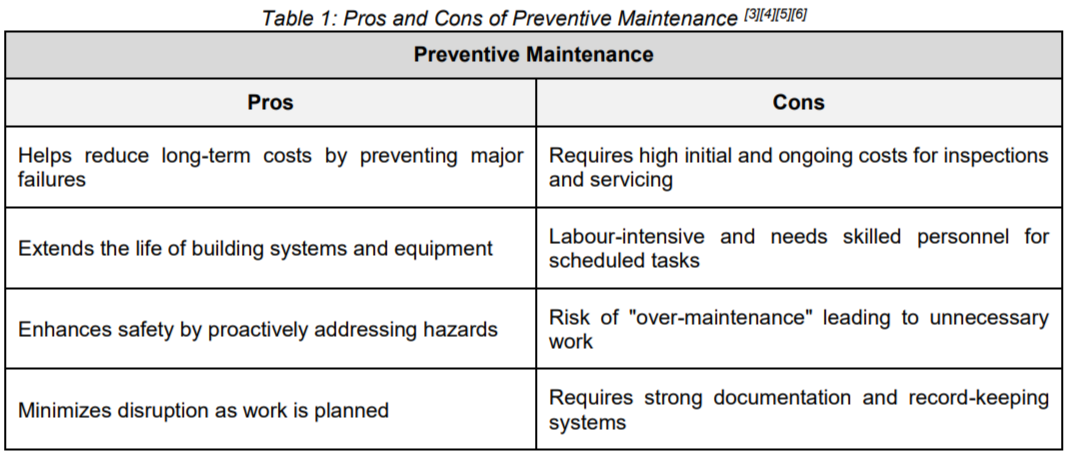
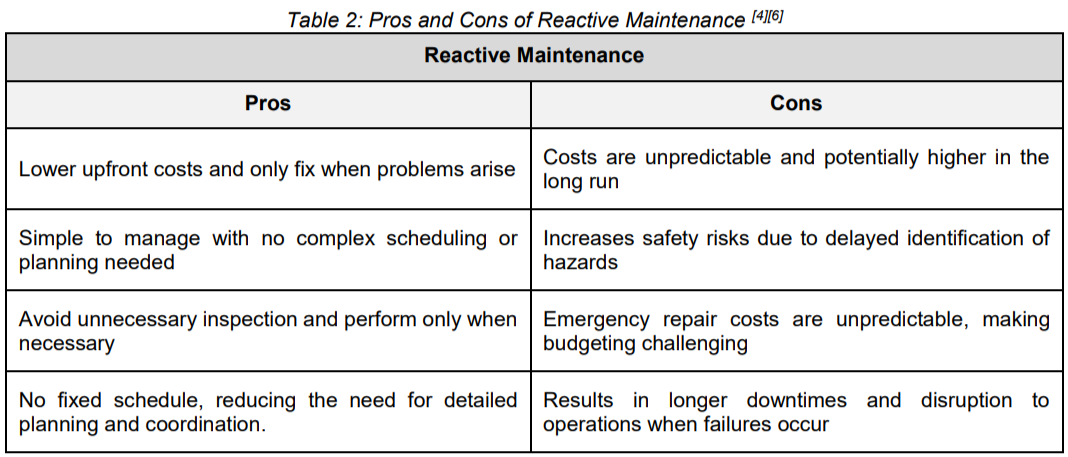
Pros and Cons of Preventive and Reactive Maintenance
As shown in Figure 1, the timing of maintenance plays a major role in how issues are handled, either preventing problems before they escalate or addressing them only after something goes wrong. Choosing between preventive and reactive maintenance isn’t always straightforward, as each approach has its own advantages and disadvantages depending on the circumstances. To clarify further, the table below compares both methods based on key factors like cost, safety, and their impact on daily operations.
Best Practices and Recommendations
Choosing between preventive and reactive maintenance isn’t always as straightforward. Each approach has its benefits, and the decision largely depends on how the building is utilized and the type of equipment involved.
For instance, reactive maintenance might make more sense in areas of a building that aren’t frequently occupied or used. If a space sees little to no activity, it’s more cost-effective to address issues only when they arise rather than commit to routine upkeep that may not be necessary.
Conversely, preventive maintenance is ideal for equipment that doesn’t require specialized skills to service. For instance, with HVAC units, basic tasks like clearing out leaves or dust from air vents can be done regularly to keep the system running smoothly without the need for expert technicians [7]. But in cases involving more complex systems, such as a printing press used in production that suddenly breaks down, reactive maintenance is the more viable option. If the right parts and technical support are readily available, scheduling repairs when needed can be both practical and efficient [7].
Instead of strictly adhering to one approach, many organizations find that a combination of both preventive and reactive maintenance works best. By integration of preventive and reactive strategies, they can balance costs, minimize unexpected failures, and maintain building performance more effectively [8].
Conclusion
In conclusion, every building will face wear and tear for all used equipment or item, it’s just a matter of when and how we choose to respond. Preventive maintenance helps us stay ahead of potential problems, while reactive maintenance allows us to act only when necessary. The key is not choosing one approach over the other, but to find the right balance based on the building’s usage, budget, and available resources. In many cases, a smart combination of both strategies offers the best of both worlds, enabling us to save costs over time while ensuring smooth operations. Maintenance is not just about fixing what’s broken; it’s also about creating a safer and more reliable environment for everyone who uses the building. With a thoughtful approach, we can achieve both goals effectively.
References
[1] ServiceChannel (2022). Preventive maintenance vs reactive maintenance: What’s the difference?. Retrieved on 18th March 2023 from https://servicechannel.com/blog/preventive-maintenance-vs-reactive-maintenance/
[2] Essam, J. (2019). Maintenance strategies and types. LinkedIn. Retrieved on 18th March 2023 from https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/maintenance-strategies-types-jean-essam/
[3] Au-Yong, C.P., Ali, A.S. and Ahmad, F. (2014). Preventive maintenance characteristics towards optimal maintenance performance: a case study of office buildings. World J Eng Technol. 2014;2:1–9. Retrieved on 18th March 2023 from https://www.scirp.org/pdf/WJET_2014091810334278.pdf
[4] Airline Hydraulics Corporation (2022). Maintenance Strategies Explained | Reactive, Preventive & Predictive Maintenance. Retrieved on 18th March 2023 from https://blog.airlinehyd.com/maintenance-strategies-explained/
[5] Gwilliam, A. (2022). Preventive vs breakdown maintenance. Retrieved on 18th March 2023 from https://www.getmaintainx.com/learning-center/preventive-vs-breakdown-maintenance/
[6] Dovetail Group (n.d.). Preventative or reactive maintenance in the UK – which is better for your industry? DTG Group. Retrieved on 18th March 2023 from https://dtguk.co.uk/preventative-or-reactive-maintenance
[7] ToolSense (n.d.). The 6 types of maintenance: definitions, benefits, examples. Retrieved on 18th March 2023 from https://toolsense.io/maintenance/the-6-types-of-maintenance-definitions-benefits-examples/
[8] Cryotos (n.d.). When to perform reactive maintenance and when not? Retrieved on 18th March 2023 from https://www.cryotos.com/blog/when-to-perform-reactive-maintenance-and-when-not
Categories
Archives
- December 2025
- November 2025
- October 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020



