Blog
What is a Strata Property?
Strata property refers to a type of development or scheme in which land or buildings are segmented into individual lots, often called ‘units’ or ‘parcels’. Common examples of strata properties in Malaysia include high-rise residential buildings like flats, apartments, condominiums, as well as townhouses. Additionally, gated and guarded community (G&G) landed properties, such as Desa Park City in Kepong, also fall under this category.
In these strata developments, important notices are frequently displayed in communal areas, including main notice boards, elevators, and mailboxes. These updates often come from the Joint Management Body (JMB), Management Corporation (MC), or Sub-MC, which are legally formed entities responsible for property management, building maintenance, and facility repair. This practice ensures that residents remain informed about various matters, such as scheduled interruptions to water and electricity supply, lift maintenance, and fogging activities, and warning notices for non-payment of maintenance fees.
While many residents recognize and acknowledge these organizations (or at least are required to), the specific roles and responsibilities of each can often be vague and confusing, especially for those who are not familiar with the industry.
What is Joint Management Body (JMB)?
A Joint Management Body (JMB) is a provisional organization established to oversee, administer, and maintain strata properties from the onset of development until the land office grants the properties strata title status. According to Section 17A of the Strata Management Act (SMA) 2013, the creation of a JMB involves collaborative efforts between the developer and the strata purchasers or owners. Their joint efforts focus on managing essential documentation, payment schedules, financial accounts, and property upkeep.
Furthermore, the inaugural Annual General Meeting (AGM) for the JMB must be held within one year following the delivery of vacant possession (VP) by the developer. The JMB will continue to function and fulfil its responsibilities until it is formally dissolved. Once the JMB is dissolved, the Management Corporation (MC) or Joint Management Committee (JMC) will take over its responsibilities.
Roles, Responsibilities, and Obligations of a Joint Management Body (JMB)
A Joint Management Body (JMB) plays a vital role in managing and maintaining strata-titled properties such as condominiums, serviced apartments, and gated communities in Malaysia. Formed jointly by the developer and property owners, the JMB ensures that all common areas, shared facilities, and building structures are properly managed until the Management Corporation (MC) takes over.
- Maintenance and Upkeep of Common Property: The JMB is primarily responsible for maintaining and repairing shared areas such as hallways, elevators, parking lots, rooftops, and building façades. This often includes engaging building repair contractors, waterproofing specialists, or structural engineers to handle issues such as water leaks, roof leaking, wall cracks, and spalling concrete. Routine inspections and preventive actions like PU injection, grouting, and waterproofing repair help extend the structure’s lifespan and prevent costly damages in the future.
- Financial Management and Oversight: The JMB manages all financial matters, including collecting maintenance fees, managing the sinking fund, and budgeting for building repair and refurbishment works. Financial records must be transparent and audited according to the Strata Management Act (SMA) 2013.
- Insurance and Legal Compliance: The JMB is required to obtain building insurance coverage and ensure that the property complies with safety standards, including fire safety and structural integrity. For older high-rise buildings, the JMB may engage engineering consultants to conduct concrete scanning, coring tests, or structural assessments to ensure compliance with local authority requirements.
- Enforcement of By-Laws and Rules: The JMB enforces building by-laws to maintain harmony and discipline among residents. This covers noise control, waste management, parking rules, and use of common areas. They may also issue notices or fines for non-payment of maintenance fees.
- Decision-Making and Administration: The JMB makes collective decisions on building upgrades, waterproofing works, repainting, and renovation of common facilities such as swimming pools and gyms. All administrative duties such as documentation, correspondence, and coordination with contractors are handled by the JMB committee or managing agent.
- Communication and Resident Engagement: The JMB serves as a communication bridge between residents, management agents, and contractors. Notices for toilet leaking repairs, waterproofing works, or scheduled maintenance are displayed on notice boards or distributed via digital platforms. The JMB also mediates resident disputes to maintain a harmonious community.
- Meetings and Representation: The JMB organizes Annual General Meetings (AGMs) and Extraordinary General Meetings (EGMs) to update residents on financial reports, project progress, and proposed building repair works. Owners can vote on budgets, appoint contractors, and elect new committee members.
- Documentation and Reporting: The JMB must maintain proper records such as the register of parcel owners, insurance policies, financial statements, and maintenance contracts. These records help ensure accountability and transparency in management decisions.
What is Management Corporation (MC)?
A Management Corporation (MC) is an organization formed by the collective unit owners of a strata-titled property, such as a condominium or serviced apartment. The MC is elected during the Annual General Meeting (AGM) and is responsible for representing all owners in managing and maintaining the common property within the development. In some cases, it is also referred to as the Joint Management Corporation (JMC).
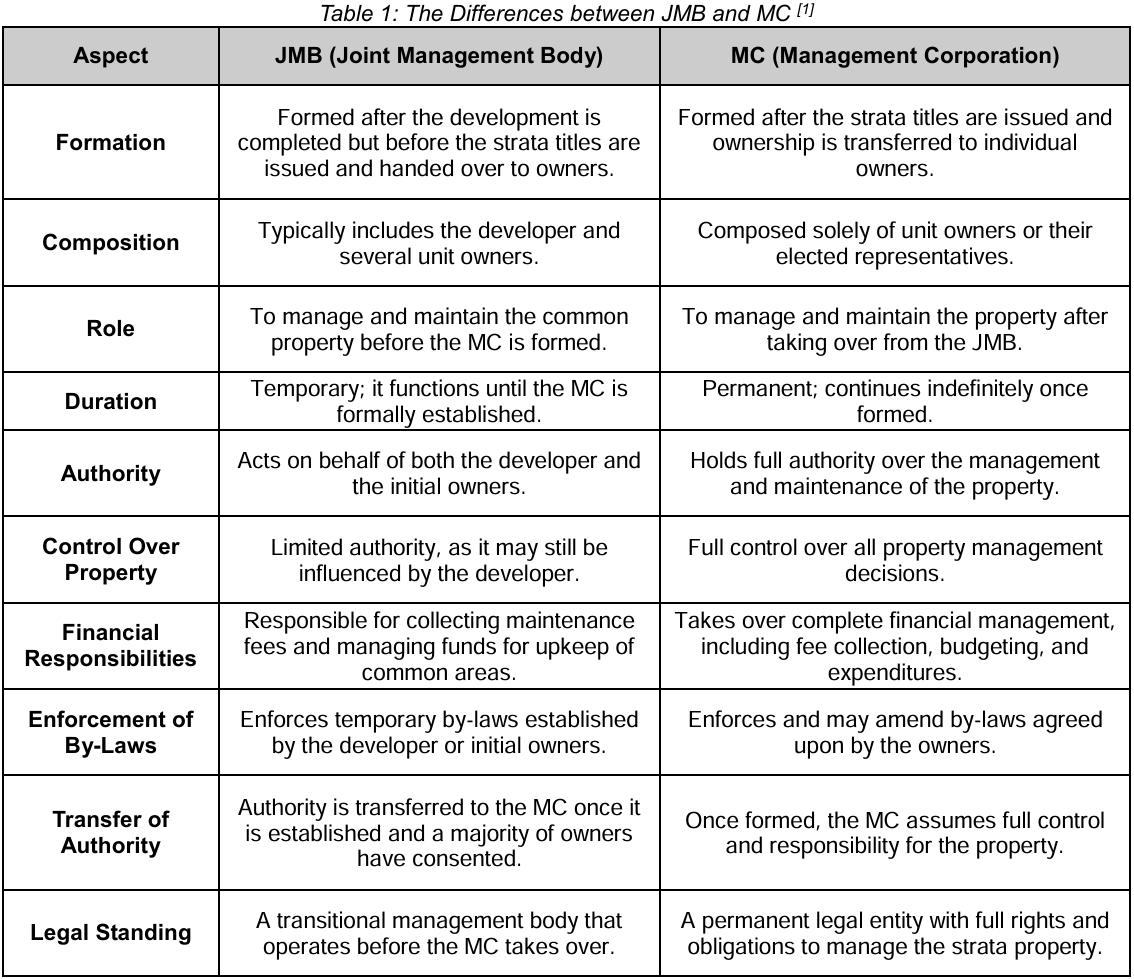
The main distinction between a Joint Management Body (JMB) and a Management Corporation (MC) lies in their timing and authority. The JMB acts as a temporary management body before the strata titles are officially issued by the land office. Once the strata title is granted and the strata register is opened, the MC is formally established to take over full management responsibilities.
The MC’s authority begins after the first AGM is held and a new management committee is elected. Subsequently, the JMB is automatically dissolved within three months. From that point onward, the MC assumes full legal control and accountability for the property’s management, covering maintenance, financial administration, enforcement of by-laws, and the coordination of repair and waterproofing works with qualified contractors or consultants when required.
While the MC’s roles, responsibilities, and obligations are generally similar to those of the JMB, the MC operates as a permanent legal entity with greater decision-making power and autonomy to ensure long-term upkeep and compliance of the strata property.
What are the Differences between JMB and MC?
What is Sub-MC?
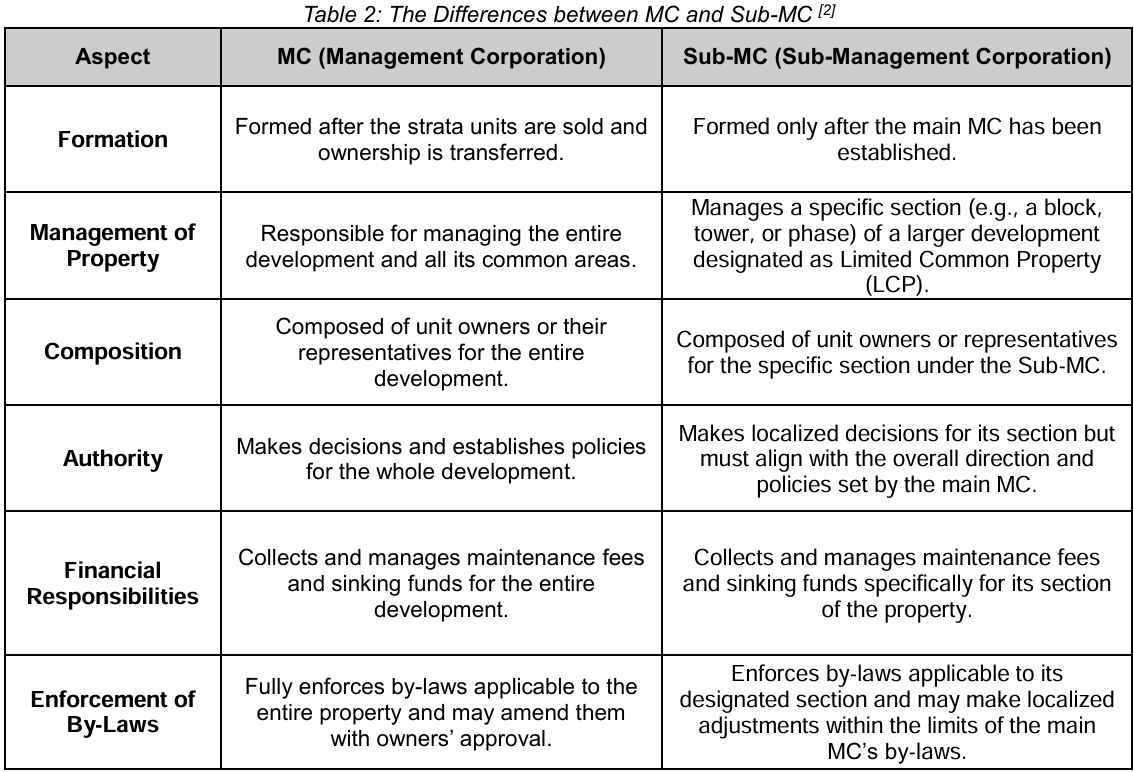
A Sub-Management Corporation (Sub-MC) is established when a development is too large or complex for a single Management Corporation (MC) to manage effectively. It governs a specific section of the property, known as the Limited Common Property (LCP), which grants exclusive usage rights to certain parcel owners.
This arrangement is particularly beneficial in mixed-use developments that combine residential, commercial, and retail components, where each section may require separate maintenance or management. A Sub-MC can only be formed after the main MC has been established. While the Sub-MC operates independently in managing its designated areas, it must include at least one representative from the main MC to ensure alignment and coordination between both entities.
What are the Differences between MC and Sub-MC?
Conclusion
In summary, the Joint Management Body (JMB), Management Corporation (MC), and Sub-Management Corporation (Sub-MC) each play essential roles in the effective management of strata properties throughout their lifecycle. The JMB oversees the initial transition from developer control to owner governance, ensuring a smooth handover process. Once strata titles are issued, the MC assumes long-term responsibility for managing and maintaining the property. In larger or mixed-use developments, the Sub-MC focuses on managing specific sections or limited common properties for greater efficiency. Together, these entities ensure that strata communities are well-maintained, financially sustainable, and harmonious for all owners and residents.
Whether managed by a JMB, MC, or Sub-MC, maintaining a strata property requires regular building inspection, waterproofing maintenance, leak repair, and structural assessment to ensure long-term safety and value. Engaging professional building repair specialists, waterproofing contractors, or structural engineers helps prevent issues such as wall cracks, roof leaks, and concrete defects, ensuring a safe and well-maintained environment for all residents.
References
[1] Properly, T. (n.d.). JMB: Joint Management Body. Properly. Retrieved on 21st July 2022 from https://properly.com.my/blog/joint-management-body-jmb/
[2] Chew, R. (2022). Know Your Stuff: What is the role of the JMB, MC and Sub MC in stratified projects? The Edge Malaysia. Retrieved on 21st July 2022 from https://theedgemalaysia.com/article/know-your-stuff-what-role-jmb-mc-and-sub-mc-stratified-projects
Categories
Archives
- December 2025
- November 2025
- October 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020



