Blog
Introduction
Building maintenance plays a crucial role in preserving the safety, durability, and value of any property. For building owners, engineers, and facility managers, a proper maintenance strategy helps prevent premature deterioration, structural damage, and costly repairs.
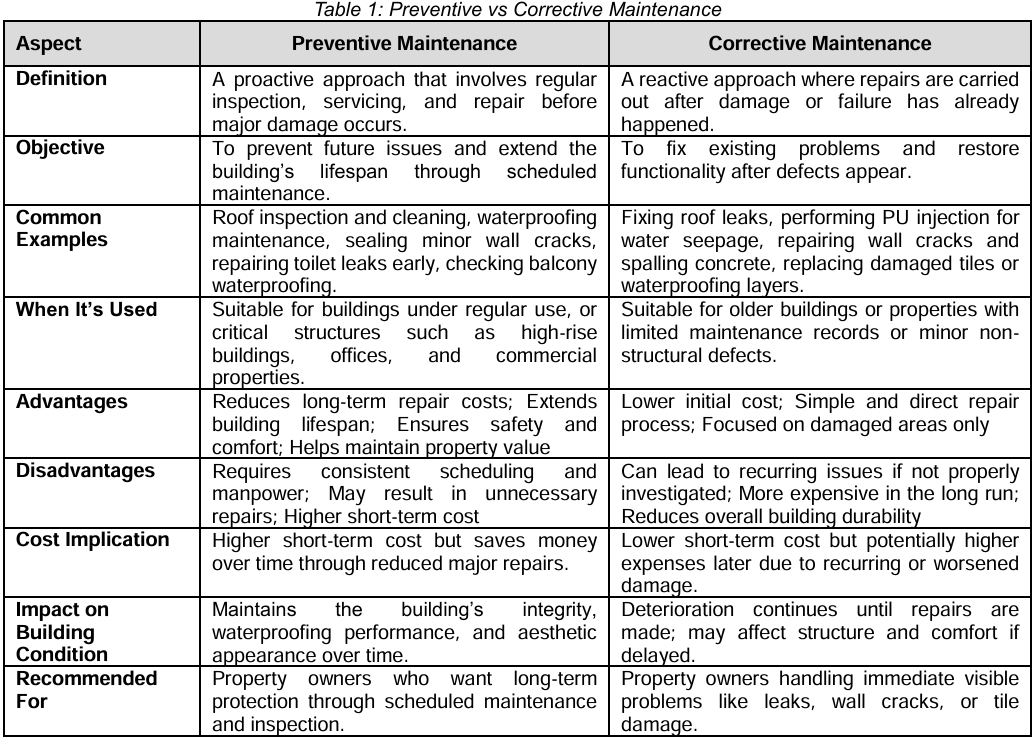
In the construction and property maintenance industry, two common approaches are used: preventive maintenance and corrective maintenance. Understanding the difference between these two methods is key to managing problems such as roof leaking, wall cracks, water seepage, tile damage, concrete spalling, and structural instability. By selecting the right approach, property owners can make smarter repair decisions, improve building performance, and extend the service life of their assets.
What is Preventive Maintenance?
Preventive maintenance (PM) is a proactive strategy that focuses on inspecting, servicing, and minor repairs before serious damage occur [1]. The goal is to detect early signs of wear and deterioration to prevent future failures.
In practical terms, preventive maintenance may include: regular roof and wall waterproofing inspections to prevent water leaking or seepage; checking tiles, walls, and ceilings for cracks, grout deterioration, or surface bubbling; inspecting balconies, toilets, and roofs for waterproofing problems before leakage spreads; monitoring wall and structural conditions to identify potential settlement or cracks.
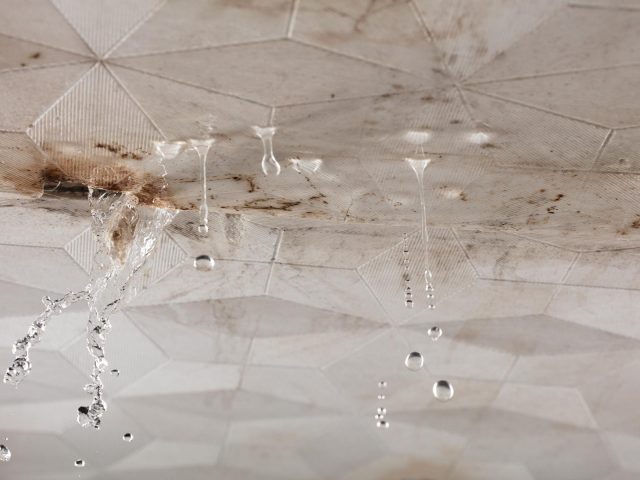
This approach helps catch problems early such as moisture seepage or wall cracks allowing for timely waterproofing repair, PU injection, or minor patch works before they evolve into larger and costlier issues [2].
Benefits of Preventive Maintenance
- Cost Savings:
Addressing small defects early such as waterproofing failures or minor cracks helps prevent serious water damage and expensive structural repairs later. For instance, fixing a small toilet leaking issue today can save thousands in future concrete or wall repair costs. [3].
- Longer Building Lifespan:
Routine checks and timely repairs by a building repair specialist help extend the structure’s life. By maintaining key components like roofs, walls, and waterproofing membranes, property owners preserve both the building’s strength and its appearance. - Improved Safety and Comfort:
Preventive maintenance reduces risks such as falling plaster, wall bulges, or roof leakage that can threaten safety. Regular upkeep ensures a safe and comfortable environment for occupants.
- Cost Savings:
What is Corrective Maintenance?
Corrective maintenance is a reactive approach which repairs are made after a problem has occurred. It focuses on resolving visible or reported issues such as roof leaking, wall crack, tile damage, or concrete spalling [4].
For example, when a ceiling leak appears, a waterproofing contractor would inspect and identify the source of water ingress, then apply suitable solutions such as PU injection, membrane replacement, or re-grouting. Similarly, if wall cracks appear, repair specialists may perform crack sealing, repainting, or surface restoration.
This approach is common in older buildings or facilities without regular maintenance records.
Benefits of Corrective Maintenance
- Lower Initial Cost
Since maintenance is only performed when problems arise, there are no recurring inspection or monitoring costs. This can be cost-efficient for smaller buildings or non-critical areas [4]. - Simple and Direct
There’s no need for complicated scheduling. Repairs are done as soon as damage is identified, allowing for fast action [5]. - Focused Resource Allocation
Corrective maintenance does not require detailed scheduling, unlike preventive maintenance. Resources can be directed specifically to the affected areas, for instance, carrying out localized tile grouting, wall crack injection, or waterproofing membrane replacement where damage is prevalent, and leaving out areas that are undamaged.
- Lower Initial Cost
Which Approach is More Effective?
Both preventive and corrective maintenance have their roles, depending on the building’s condition, age, and usage.
For critical areas like roofs, balconies, car parks, and toilets, preventive maintenance is the better choice. Regular inspections, waterproofing checks, and minor repairs help prevent major failures.
However, corrective maintenance can be practical for non-critical areas such as decorative finishes or small wall touch-ups. The best strategy is a balanced approach, combining preventive maintenance for key components with corrective repair when necessary.
Regular inspections by a building repair specialist ensure problems like roof leaks, wall cracks, and water seepage are identified early and resolved properly. Working with an experienced waterproofing contractor or repair specialist ensures the right solution for each issue, protecting both the structure and your investment.
Conclusion
A well-maintained building not only looks better but also lasts longer and provides a safer environment for its occupants. While preventive maintenance helps avoid costly breakdowns, corrective repair remains necessary for unexpected damages.
Ultimately, combining both approaches offers the best results, preventive maintenance to minimize future risks, and corrective repair to handle immediate issues.
By engaging professional services such as roof repair, waterproofing repair, PU injection, wall crack repair, and balcony repair, building owners can protect their properties effectively and ensure long-term structural integrity and comfort.
References
[1] Maiti, S. (2020). What is Preventive Maintenance? Advantages and Disadvantages of Preventive Maintenance. Education Leaves. Retrieved on 21st June 2022 from https://educationleaves.com/what-is-preventive-maintenance/
[2] UpKeep (n.d.). The Advantages & Disadvantages of Preventive Maintenance. Retrieved on 21st June 2022 from https://upkeep.com/learning/benefits-of-preventive-maintenance/
[3] Service Channel (n.d.). 7 Benefits of Preventive Maintenance for Facilities. Retrieved on 21st June 2022 from https://servicechannel.com/blog/benefits-of-preventive-maintenance/
[4] UpKeep (n.d.). What is Corrective Maintenance? Definition & Examples. Retrieved on 21st June 2022 from https://upkeep.com/learning/corrective-maintenance/
[5] TWI (n.d.). What is Corrective Maintenance? (Definition, Pros, Cons and Examples). Retrieved on 21st June 2022 from https://www.twi-global.com/technical-knowledge/faqs/what-is-corrective-maintenance#WhenisCorrectiveMaintenanceNeeded/
Categories
Archives
- December 2025
- November 2025
- October 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020



