Blog
Introduction
In a tropical country like Malaysia, where the weather is hot and rain occurs frequently, this can cause concrete cracks due to the continuous expansion and contraction of the concrete from the temperature change. Even though some of these cracks are very minor, water still can seep through the concretes easily and thus causing leakage. To add extra protection against water leakage, membranes can be generally used in roofs, toilets, or any other structures that require waterproofing effects or weather protection. The two types of membranes are sheet-based membranes and liquid-based membranes. Both types of membranes have their pros and cons and will be further discussed in this article.
WHAT IS SHEET-BASED MEMBRANE?
A sheet-based membrane is in a form of sheet rolls. It can be made of bitumen, thermoplastic, thermosetting material or rubber. Sheet-based membranes are differentiated by the way it adheres against the surface, such as follows:
Torch Applied Membrane
- Requires a heated torch to melt the layer onto the surface.
- The melt membrane is very adhesive and can stick firmly to the surface when it cooled.
Self-Adhesive Membrane
- Covered by a release liner, which is to be removed when applying on the surface.
- Cold-applied alternative which is safer during the application work.
WHAT IS LIQUID-BASED MEMBRANE?
A liquid-based membrane comes in a liquid form as the name suggested. It can be applied through a roller, spray, or brush. When the membrane is dried up, a waterproofing layer will be formed. The liquid-based membrane may be used to heal leaks and cracks due to its capability to blend into the applied surface. Some liquid-based membranes are:
Water-based
- Typically takes the form of water, which is non-toxic.
- Solvent-based
- Typically takes the form of a chemical solvent to have chemical reactions when exposed to air.
Polyurethane
- An elastic waterproofing membrane which is made of high polymer material enhanced with a certain quantity of modifier.
- Good resistance to abrasion, chemical, UV, and bio-degradation.
Cementitious based
- Needs to be mixed with the right proportions of cements, water, and aggregates before applying to the surface, but it is vulnerable to joints and cracks.
- It also required enough membrane thickness to ensure excellent waterproofing quality.
- It is a kind of modified cementitious product, made by incorporating polymer additive.
- The polymer fills the pores in the concrete mix to make it more watertight, durable, and increase its tensile strength.
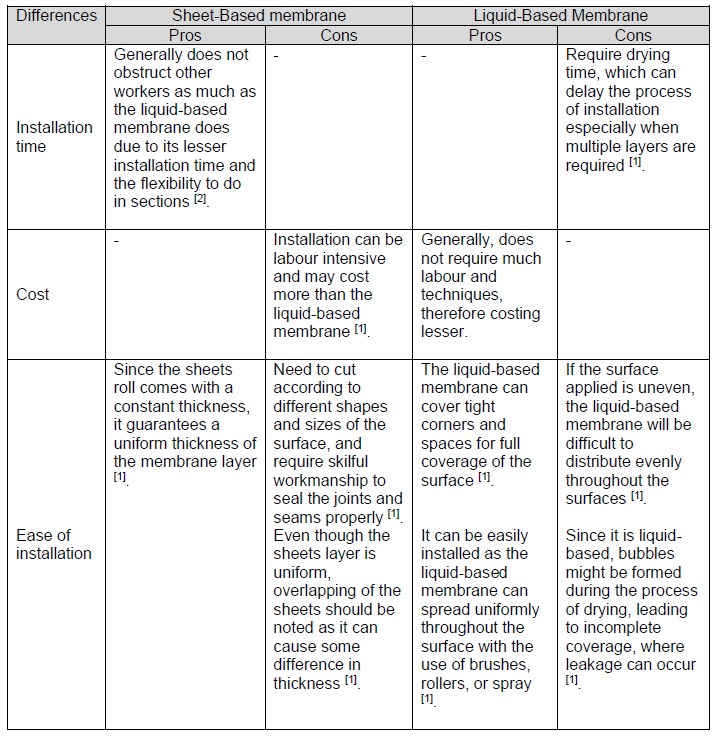
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INSTALLATION TIME, COST, AND EASE OF INSTALLATION
Conclusion
Overall, neither one of them is better than the other as long as it works well in both weather and waterproofing. To choose the most suitable option of the membrane, it all depends on the type of projects, weather, time allowance, budget, development conditions, and requirements.
References
[1] Sheet vs Fluid Applied Waterproofing. Retrieved on February 17, 2020, from https://www.tremcocpg-asiapacific.com/news/sheet-vs-fluid-applied-waterproofing
[2] Sheet Membrane Benefits: Sheet vs Liquid: CCL Wetrooms. Retrieved on February 17, 2020, from https://www.ccl-wetrooms.co.uk/blog/benefits-sheet-membranes-sheet-vs-liquid-2/
[3] Wikimedia Commons. Tar Sheet Bsed Waterproofing.JPG. Retrieved on February 18, 2020, from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tar_Sheet_Bsed_Waterproofing.jpg
[4] Wikimedia Commons. Liquid Rubber Europe Coatings.JPG, Retrieved on February 18, 2020, from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Liquid_Rubber_Europe_coatings.JPG
Categories
Archives
- December 2025
- November 2025
- October 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020